How it works: Workload migration
The information described in this page is not necessary knowledge for using OS Migrate workload migration. However, knowing how the migration works under the hood may be useful for troubleshooting or forming deeper understanding of OS Migrate.
Data flow
The workload migration utilizes so called conversion hosts to transfer data from the source cloud to the destination cloud.
The conversion hosts are temporarily deployed in the source & destination projects. Being in the same project as the source (and destination, respectively) VMs ensures that the conversion hosts will have access to the data that needs to be migrated (snapshots and volumes).
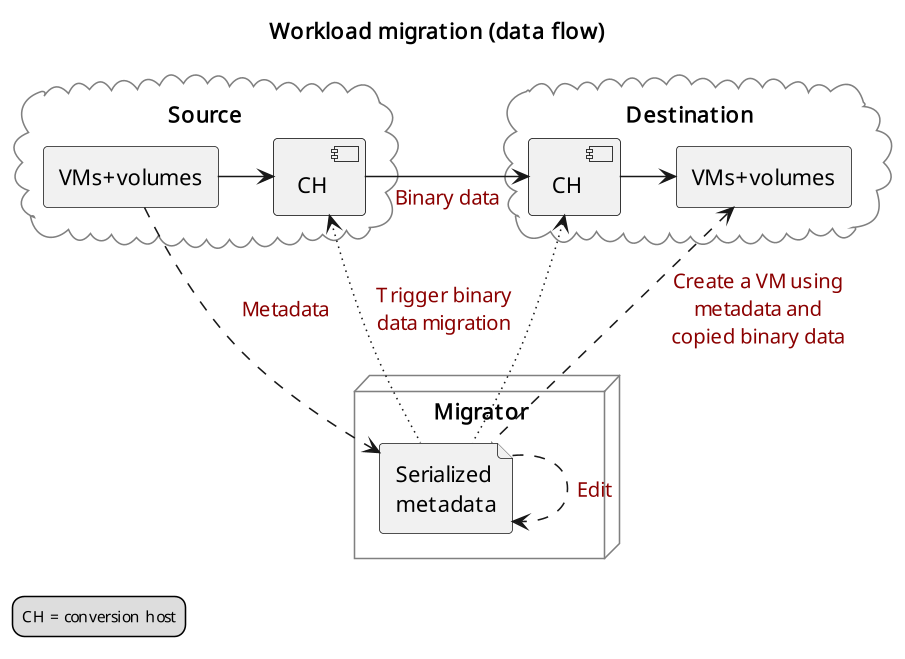
Workload migration (data flow)
Migration sequence
The export_workloads.yml playbook simply exports workload metadata
into workloads.yml.
The actual main migration sequence happens inside
import_workloads.yml playbook and the import_workloads
role. The initial common steps are:
The resources loaded from
workloads.ymlare validated.Resources are filtered according to
os_migrate_workloads_filter.Reachability of source & destination conversion hosts is verified.
If you’re defaulting to the default storage migration mode data_copy
then the role starts iterating over all workloads that passed the
filter. The steps performed for each workload (Nova Server) are:
The
import_workload_prelimmodule creates log and state files under{{ os_migrate_data_dir }}/workload_logs. It also takes care of skipping migration of VMs that already exist in the destination, and skipping of conversion hosts, should such migration be attempted.The
import_workload_dst_checkmodule checks whether migration prerequisites are satisfied in the destination cloud/project. This means verifying that resources which are referenced by name from the workload serialization can be de-referenced in the destination cloud. In other words, this verifies the networks, subnets etc., that the destination VM should be attached to, indeed exist in the destination cloud.If
os_migrate_workload_stop_before_migrationistrue, the VM in the source cloud is stopped.The
import_workload_src_checkchecks whether the source workload is ready to be migrated. This means verifying that the Nova Server isSHUTOFF.The
import_workload_export_volumesmodule prepares data for transfer to the destination cloud:If
boot_disk_copyistrue, a snapshot of the source VM is created, converted to a Cinder volume and attached to the source conversion host.Additional Cinder volumes attached to the source VM are detached from it and attached to the source conversion host.
All VM’s volumes (boot & additional) on the conversion host are exported as NBD drives, listening on localhost only.
The
import_workload_transfer_volumescopies data from source to destination:SSH port forwarding is created for the NBD drives of the source conversion host, so that they are accessible on the destination conversion host, again on localhost only. (The data transfer mechanism could be described as “NBD over SSH”.)
Cinder volumes are created in the destination project for both the boot disk and additional volumes (as applicable). The destination volume sizes match the volume sizes in the source cloud. The volumes are attached to the destination conversion host.
Sparsification of the NBDs is performed, only for recognizable filesystems that the
virt-sparsifytool supports. This significantly speeds up copying of empty space on supported filesystems.Data is copied from the NBDs to the respective destination Cinder volumes.
SSH port forwarding for the NBDs are closed, and volumes are detached from the destination conversion host.
The
import_workload_create_instancecreates new Nova server in the destination cloud according to the data from the resource serialization, and using the copied Cinder volumes as applicable.The
import_workload_src_cleanupcleans up after the migration in the source cloud. It closes the NBD exports, detaches volumes from the conversion host, deletes the temporary boot disk snapshot volume and re-attaches any additional volumes back onto the source VM (as applicable).In case of failure during the migration, the
import_workload_src_cleanupmodule is executed too, and an extraimport_workload_dst_failure_cleanupmodule is executed, which aims to clean up failed partial migration from the destination cloud. (In case of successful migration, no further clean up is necessary in the destination cloud.)

Sequence diagram of workload migration internal actions